What is Diaphragm Spasm?
Diaphragmatic spasm is best understood as a problem and as a health risk when one best understands the very significant role of the diaphragm in the human body. The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscular organ which is vital for respiration and is mainly responsible in separating the thoracic cavities and abdominal cavities.
Diaphragm Functions/what does the diaphragm do?
There are three important functions in the contraction of the diaphragm:
- It becomes flattened when contracting to facilitate the decrease of intrapleural pressure.
- The volume of the thorax is increased or expanded in size as it is located in the inferior aspect of the thorax.
- It supports the lungs as it inflates during breathing, facilitating air to get into the lungs.

Diaphragm Spasm is associated with different forms such as synchronous diaphragmatic spasm, an epidemic transient diaphragmatic spasm or a transient or temporary diaphragmatic spasm. A decrease in diaphragmatic function will always end up with a respiratory malfunction of the person.
Signs and Symptoms
Diaphragm Spasm can take in any form of its presentation either as a hiccup or diaphragmatic synchronous flutter, as a diaphragmatic strain, or the form which is known as getting the wind knocked out of a person.
Diaphragmatic strain leads to the formation of hiatal hernia which can result to diaphragm weakness, problems of the heart and circulation, cases of acid reflux or it can be gastroesophageal reflux disease or abbreviated as GERD. The GERD develops as a consequence 0f some prescribed medications that minimizes the formation of acid in the stomach.
Hiatal hernia on the other hand can be resolved in just a few minutes if correctly and immediately diagnosed, by allowing the diaphragm to simply stretch by itself into the normal position in less than two minutes.
Hiccups are often the result of a full stomach. This causes an irritation in the phrenic nerves, inducing diaphragmatic spasm. The excess amount of food and air being swallowed distends the stomach, thereby causing the irritation. The intake of some hot and spicy foods is also believed to irritate the phrenic nerves.
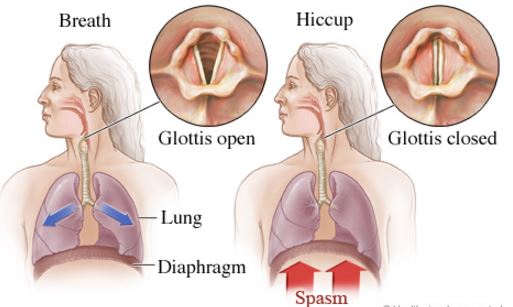
Other conditions which might result into hiccups are the excessive smoking habit of a person and too much alcohol consumption, getting stressed, feelings of shock from trauma or accidents, some emotional excitements and other related feelings can lead to hiccup. If a person experiences the hiccups more than 48 hours, it is always advisable to seek medical consultation.
Another instance which may lead into Diaphragm Spasm is the application of a sudden forceful blow into one’s abdomen. This usually happens when the person is involved with some type of contact sports where a sudden force can create a very strong blow of pressure in the abdomen or may hit the solar plexus region of the abdomen.
Causes
Diaphragmatic excursion has to be within normal to prevent respiratory compromise with diaphragmatic functions. Diaphragmatic problems can occur in cases where there is something wrong with neurologic and anatomic functions of the diaphragm.
These problems can be due to a traumatic injury or disease process involving the diaphragm or in the existence of some anatomic disorders.
Diaphragm Spasm can be due to a hiccup of the person resulting from different factors, any forms of diaphragmatic strain or anything that blows out a person through a sudden force applied in the abdomen.
Medical Treatment
Treatment is made based on what causes the Diaphragm Spasm of the patient. Management can be done through:
Physical pushing of the diaphragm is needed for hiatal hernia to make the diaphragm back into its proper place.
Individuals who are having hiccups may have home treatment. Hiccups which last more than 48 hours have to seek medical advice for assessment of its cause and for proper treatment.
Pain relievers or some alternative therapy are utilized to minimize the discomfort for those with sudden blows in the abdomen that causes the knock out of the person.
References:
Diaphragm Spasm treatment at http://insidetheclinic.com/diaphragm-spasm/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hiccup
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Getting_the_wind_knocked_out_of_you
MacAuley, D (2007). Oxford Handbook of Sport and Exercise Medicine. Oxford University Press. p. 572.
Shultz, Sandra J.; Houglum, Peggy A.; Perrin, David H. (2005). Examination of Musculoskeletal Injuries. Human Kinetics. p. 567.
Straus C, Vasilakos K, Wilson RJ, Oshima T, Zelter M, Derenne JP, Similowski T, Whitelaw WA (February 2003). “A phylogenetic hypothesis for the origin of hiccough”. BioEssays 25 (2): 182–188.
