What are Hemorrhoids?
Talking of hemorrhoids, they are swollen veins in an individual’s anus or the lower rectum, and are similar to varicose veins. They are also referred to as piles. There are various causes of hemorrhoids, but most often the cause is unknown. For example, you may have hemorrhoids that occur due to straining when having bowel movement, they may also occur when there is increased pressure on the veins at time of pregnancy.
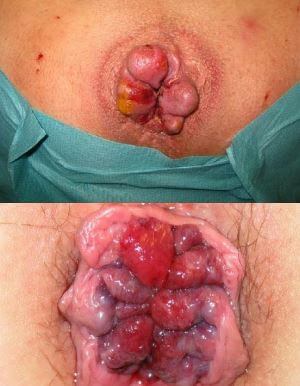
External Appearance of hemorrhoids at anus
You may have hemorrhoids inside the rectum, also known as internal hemorrhoids, or you could have them develop just under the skin surrounding the anus, also known as external hemorrhoids. Many people have hemorrhoids, so they are very common. It is believed that at least three out of every four adults are going to have hemorrhoids during their life 1.
While at times, piles don’t cause symptoms, at other times, they can cause discomfort, itching, bleeding, and pain. Occasionally, you may have hemorrhoids that have a clot and they are referred to as thrombosed hemorrhoids. These may not be dangerous, however, they can be extremely painful, which often calls for lancing and draining. That said, hemorrhoids don’t have to make your life miserable because there are many treatment options available. In fact, many people are able to get relief and manage the symptoms using home treatments or just change in lifestyle.
Some key points you want to note about hemorrhoids is that women have increased chances of developing hemorrhoids while pregnant and that as a person ages, their likelihood of having hemorrhoids increases. At times surgery may be needed if conventional treatment methods and home treatment do not work or if the piles are so severe. Although hemorrhoids can be unlikable and painful, it is easy to treat and prevent them.2
If your hemorrhoid pain, then you are not alone, even Napoleon had them, something that distracted him because of severe pain at time of his conquer at Waterloo3.
Types of Hemorrhoids

Hemorrhoids may be classed depending on their location and other characteristics.1
Internal hemorrhoids
With internal hemorrhoids, they originate in the rectum. They are located inside of an individual’s rectum. That means you cannot see or feel them, and in most cases, they don’t cause discomfort. Sometimes, when you strain or if there is irritation when you pass stool, it may damage the surface of hemorrhoids and result in bleeding. Hemorrhoids are regarded as the commonest cause of rectal bleeding. At times, straining may cause internal hemorrhoids to push through the anal opening, and these are referred to as prolapsed or protruding hemorrhoids. These can be painful and irritating.
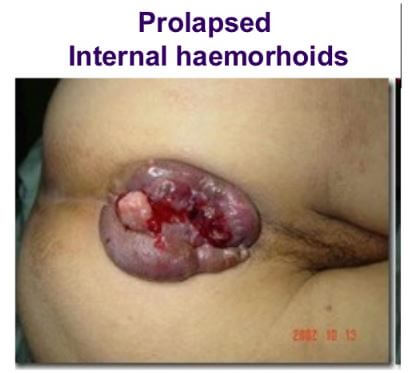
Prolapsed Internal hemorrhoid
External hemorrhoids
When you talk of external hemorrhoids, they are those originating in the anus. When there is engorging or enlargement of vessels occurring under the skin found around the anus, they are referred to external hemorrhoids. If these hemorrhoids are irritated, they are likely to bleed and itch. Because the skin in the region of the anus has more sensitive nerves (pain-sensing nerves), it makes the external hemorrhoids to be more painful.
External hemorrhoids can bring problems, especially when they are thrombosed or have clotting. The thrombosis causes an anal lump to form, and it’s very painful and tender. A thrombosed hemorrhoid has scarring when it heals, it may leave a skin tag that protrudes in the anus. The tag may at times enlarge making the cleaning of the anal area a difficult thin.
Thrombosed hemorrhoids
In an external hemorrhoid, you may find blood that has pooled forming a clot or thrombus, this may result in severe pain, inflammation, swelling, and a kind of hard lump forming near the anus.
Symptoms of Enlarged Hemorrhoids
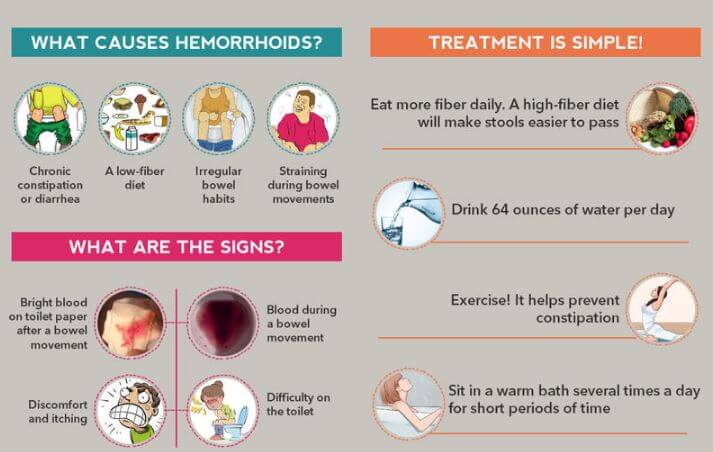
Symptoms, Causes & Home remedies of Hemorrhoids
When you have enlarged hemorrhoids, the symptoms may involve1,3:
- Itching and irritation around the anus
- Burning sensation at the anus
- Mucus discharge
- Severe pain
- Bleeding without pain – you may see some bright red blood spots on the toilet tissue or even on the toilet bowl
- Having a sensation that your bowel isn’t like empty
- Swelling around the anus
- Have moist, pink pumps forming on edges of the anus or bulging out, these may also assume a purple or bluish look4.
Causes of Hemorrhoids
Some people are likely to develop hemorrhoids if there are family members who had them, for example, if your parents had them. When there is buildup of pressure, especially in the lower rectum, it affects the flow of blood making the veins to start swelling. The pressure may result from:1,2,3,4,5,6
- Extra weight or obesity
- Pregnancy
- Bowel movement
- Straining or holding your breathe when taking on a hard physical activity for example, lifting something heavy
- Low fiber diet
You may be at risk of getting hemorrhoids if you sit or stand for long stretches. Also, you may have piles when you diarrhea or constipate for an extended time. Sneezing, coughing, and vomiting may worsen the hemorrhoids.
How Diet Contributes to Hemorrhoids?
The kind of food you take impacts your susceptibility to get hemorrhoids. If you take a diet that has high fiber, it is less likely that you will have hemorrhoids, however, if you are accustomed to taking a diet consisting of processed foods, then you face a higher risk of getting hemorrhoids.
Having a low-fiber diet may lead to constipation, which in turn may make you get hemorrhoids because constipation makes you strain on the toilet and aggravates the hemorrhoids because of hard stool. The hard stool arising due to constipation further irritates the veins making them inflamed and even painful.3
Bleeding Hemorrhoids
One of the signs and symptoms of hemorrhoids is bleeding that isn’t accompanied by pain (painless bleeding). You may see some bright red blood on toilet paper, on the stool surface, or dripping into the toilet. The bright red blood shows that the bleeding is occurring in the lower gut and hasn’t been digested or has not passed through the stomach and intestines. If it had passed through stomach and intestines, it would appear in stool as black, tarry stool (melena).
Hemorrhoid bleeding resolves by itself without needing treatment, however, if you have bleeding occurring when you have a bowel movement, it is important that you check with a doctor. Hemorrhoids are the commonest cause of bleeding when having bowel movement, however, it can also be a sign of other serious conditions such as:3
- Infection
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Tumors.
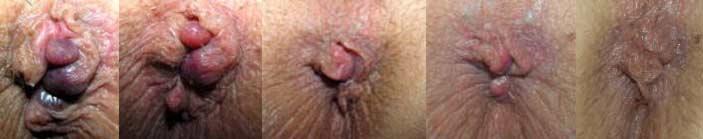
Hemorrhoids Classification
To help determine the kind of pain an individual having hemorrhoids is experiencing, doctors use a kind of grading system that runs along four stages, and they include:3
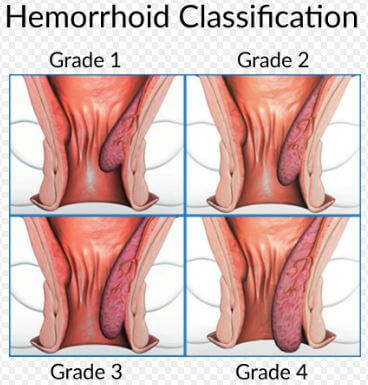
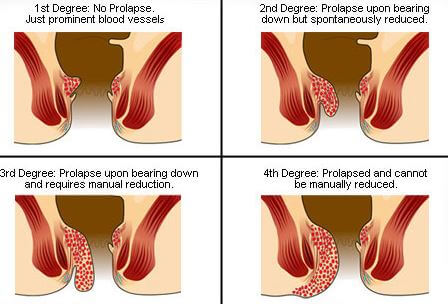
Classification/Grades of Hemorrhoids
First-degree hemorrhoids
When you have hemorrhoids that bleed, though they don’t prolapse or protrude outside of the anus, it is called 1st degree hemorrhoids. These hemorrhoids are slightly engorged or enlarged.
Second-degree hemorrhoids
When an individual has hemorrhoids that prolapse but retract back on their own, then it is the second grade of hemorrhoids. In this case, they bleed or do not bleed. The piles will protrude when you take certain activities for example, when you are passing stool and they return back to the rectum.
Third-degree hemorrhoids
You have grade three hemorrhoids if they protrude after you take on some activities like passing of stool, but you have to push them back in using your finger.
Fourth-degree hemorrhoids
If you have hemorrhoids that when they prolapse, they cannot be retracted or pushed back in to the anal canal, it is said that you have the fourth class of piles. In this class, it includes the thrombosed hemorrhoids or those that pull a great amount of rectum lining through the anus.
Recent studies indicate that patients having hemorrhoids have an anal canal tone that has a higher rest. What this means is that the smooth anal canal muscle tends to remain tighter than it should, even when an individual is not straining. Constipation aggravates the problem because the bowel movement creates pressure that pushes the hemorrhoids to the sphincter muscle. The hemorrhoids bulge or prolapse when the connective tissues supporting and holding the hemorrhoids weaken with age.5
Diagnosis of Hemorrhoids
To diagnose a patient of hemorrhoids, a doctor will make examination of the anal canal and the anus. The doctor will ask questions about when you started noticing blood or feeling lumps and if you experience any form of pain. The doctor will want to know if the hemorrhoids come out and retract on their own or not. It is important that a doctor excludes other conditions that may have symptoms similar to those of hemorrhoids, for example:
- Fistulae
- Anal fissures- it is estimated that about 20 percent of patients who have hemorrhoids, they have a fissure too6.
- Infections
- Perianal skin diseases (those occurring around the anus)
- Tumors
The doctor may feel the inside of your anus using a finger that has a lubricated glove or use some other instrument.3,5
- Anoscope: An anoscope is used to view areas of the lower rectum, the lower few inches. It’s a hollow, lighted tube.
- Proctoscope: To look deeper into the rectum, a doctor may use an instrument called proctoscope, that although works like anoscope, it can see deeper.
- Sigmoidoscopy: This is an instrument that looks at the sigmoid or lower colon. It’s flexible.
- Colonscope: It allows the doctor to view the entire color. It’s a flexible, lighted tube.
- Barium X-ray: This is able to show entire inside of a patient’s colon.
Sigmoidoscope and colonoscopy are performed if there is evidence suggesting rectal bleeding or presence of microscopic blood within the stool. These instruments help to rule out any possibilities of other conditions causing bleeding for example, cancer or colorectal polyps.
Home Remedies for Hemorrhoids
If you have hemorrhoids that have not advanced to more severe cases, you can treat the symptoms using simple, home remedies. These home remedies for hemorrhoids will prevent occasional flare-ups. 3,4,5,6

More fiber diet
You need to get more fiber into your diet by taking fiber supplements such as Citrucel, Metamucil, or Fiber Con. Also, ensure that you have sufficient fluid to help fiber to soften stool and allow you to easily have bowel movements. Also it helps reduce pressure on the hemorrhoids, something that otherwise could worsen them.
Fiber supplements can help minimize bleeding of hemorrhoids or enlargement and inflammation. Fiber supplements also help to reduce irritation that may be caused by small pieces of stool trapped around the vessels.
You can also take high-fiber foods including beans, broccoli, oat bran, wheat, whole grain, and fresh fruits. If you find that you are having gas or bloating when you increase fiber intake, you can start slowly and then gradually step up the intake to about 25 to 30 grams fiber in a day. Let this go hand in hand with fluid intake, to ensure the fibers work effectively.
Have moderate exercise
You don’t have to get into grueling exercises because they can put pressure on the vessels when the muscles are overworked. So, you want to have moderate aerobic exercises for example, having brisk walk that lasts about 20 to 30 minutes every day. This helps with bowel function.
Have a regular bowel habit
Whenever you have the urge to defecate, you need to go to the toilet immediately. It’s advisable that you don’t hold stool because it can back up creating strain and pressure. Ensure you try to establish a time when you have bowel movement for example, after having a meal.
A sitz bath
Taking a warm water bath of the hips and buttocks helps to relieve irritation, itching, and spasms of sphincter muscle. There are small plastic tubs sold in pharmacies that can fit over your toilet seat.
Alternatively, you can sit in the typical bathtub filled with some warm water, at least a few inches. It’s recommended that you have around 20-minutes of a sitz bath following a bowel movement, then three more times in a day. Make sure that you dry the anal area gently, avoid rubbing or wiping hard. Your hair dryer may help to pat dry the anal area after the sitz bath.
Topical relief
There are over-the counter creams that are made for treating hemorrhoids. These contain a local anesthetic that will temporarily help to soothe pain. Again, suppositories and creams containing hydrocortisone may be effective, however, you are not advised to use them in more than a week because they can lead to skin weakening.
Witch hazel wipes tend to be soothing and contain no harmful side effects. You may use small ice whereby you place it on the anal area, at least for some few minutes, it will help to reduce the pain as well as swelling. Alternatively, you can sit on a cushion instead of hard surface, this helps to ensure existing hemorrhoids don’t swell. It also prevents new hemorrhoids from forming.
Treating the clot
If there is a blood clot, it makes the hemorrhoids to be more painful. In case the pain seems to be tolerable, you can wait for it to disappear on its own, this is especially so if the clot has persisted for more than two days. Just apply home treatment to relief the symptoms. Moreover, if you have had a clot that is more recent, then a surgery may be needed to treat the hemorrhoid or a minor procedure may be performed to withdraw the clot from the vein.
Minimally Invasive Hemorrhoid Treatments
Sometimes, you may find that the hemorrhoids cannot be managed using conservative treatment because you have symptoms that have persisted for a longer period or there is prolapse of internal hemorrhoids. Minimally invasive treatments tend to be less painful compared to the traditional removal of hemorrhoids through hemorrhoidectomy. The procedures also allow for quicker recovery and they are performed as an outpatient surgery or in surgeon’s office.3,5
Rubber band ligation
This is a common procedure for treating hemorrhoids. It uses a small elastic band that is placed around the hemorrhoid base. The band shrinks the hemorrhoid and the tissue surrounding it forming a scar as it heals, this helps hold the hemorrhoid in place.
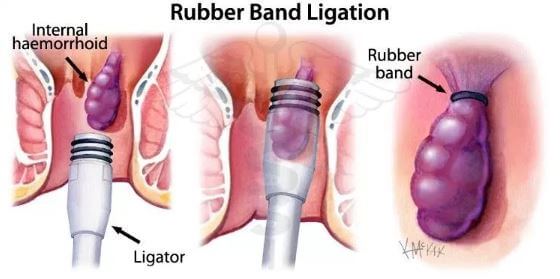
A patient may need about two to four procedures performed eight weeks apart for the hemorrhoid to be completely eliminated. In this procedure, there may be some complications, though rare, and they include mild pain and tightness, but this can be relieved by having a sitz bath. Infection and bleeding may also occur, but again, they are rare.
Other procedures that are performed in a surgeon’s office and which work on a similar way like the rubber band ligation are infrared or laser coagulation, cryosurgery, and sclerotherpay. However, these may not prevent the recurrence of the hemorrhoids.

Management Options of hemorrhoids
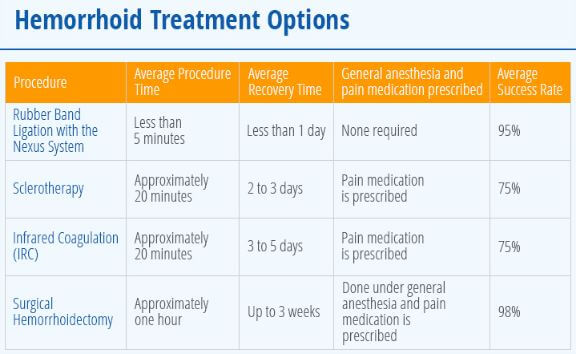
Surgical Options of Hemorrhoids with Recovery time & Success rates
Traditional Surgery for Hemorrhoid
Hemorrhoidectomy
The common surgery for hemorrhoid is hemorrhoidectomy, it is preferred if a patient has large prolapsing or protruding hemorrhoids. It is also recommended if an individual has persistently symptomatic hemorrhoids that occur externally or for the case of internal hemorrhoids that recur despite having rubber band ligation. During this surgery, a surgeon makes a narrow incision around the hemorrhoid tissue (external or internal hemorrhoid) where the affected blood vessels are taken away.
Traditional hemorrhoidectomy has lower complication rates and cures about 95 percent of hemorrhoid cases. It is also painful and therefore a general anesthesia is required. Patients are able to go home same day. After the procedure, a patient may resume work in about 7 to 10 days.5
Stapled hemorrhoidopexy
This is an alternative to the traditional hemorrhoidectomy, and it is done if a patient has prolapsed or bleeding hemorrhoids. In this procedure, a surgeon uses what is known as a stapling device that anchors the hemorrhoids right in their typical position. A general anesthesia is used in the procedure.
Non-Surgical Treatments
Heat Coagulation
A doctor may use heat to help destroy the hemorrhoidal tissue while also promoting inflammation and scarring. The non-surgical treatments include:
- Infrared photocoagulation
- Bipolar diathermy
- Direct-current electrotherapy.
With these procedures, they will destroy the tissue found in and around hemorrhoids causing scar tissue. The procedures are used with grade I, grade II, and grade III hemorrhoids. A patient will feel pain but is less compared to rubber band ligation. Also, bleeding is likely to occur.3
Reference List
- Hemorrhoids. Available at https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hemorrhoids/symptoms-causes/syc-20360268
- Hemorrhoids: Causes, treatments, and prevention. Available at https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/73938.php
- Hemorrhoids: An Illustrated Guide to Treatment. Available at https://www.onhealth.com/content/1/hemorrhoid_treatment
- What Are Hemorrhoids? Available at https://www.webmd.com/digestive-disorders/understanding-hemorrhoids-basics#1
- Hemorrhoids and what to do about them. Available at https://www.health.harvard.edu/diseases-and-conditions/hemorrhoids_and_what_to_do_about_them
- Hemorrhoids: A Common Clinical Problem. Available at https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/829350
